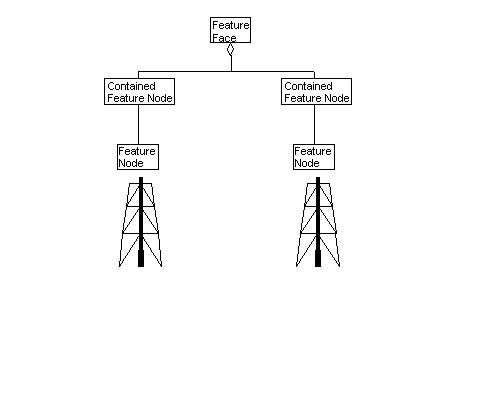
Class Name: Contained Feature Node
Definition
The one-directional topological relationship between a
Feature Face and a
Feature Node that is contained within its
boundaries.
Primary Page in DRM Diagram:
Example
- A Feature Face representing part of an ocean
contains two Feature Nodes, which represent two
oil platforms. The Feature Face must have 2
Contained Feature Node components,
which in turn must have the 2 Feature Nodes as
components. Note that each of the 2 Feature
Nodes would have Contained
Within Feature Face components, which would be associated with the
Feature Face.
FAQs
- When is a Contained Feature
Node object required?
- At feature topology levels
3
and
4, a Feature Face object is required to
have a Contained Feature Node
component for each Feature Node that is
located within its boundaries. At feature topology levels
0
through
2,
the Contained Feature Node component
is optional. Also, if a Feature Face does not
contain any Feature Nodes within its boundaries,
it must not have any Contained Feature
Node components.
- Can the same Feature Node be a component
of more than one Contained Feature
Node object?
- No. Since a Feature Node can only be located
within the boundaries of one Feature Face, it
may only be a component of a single
Contained Feature Node object.
- What is the relationship between the
Contained Feature Node class and the
Contained Within Feature Face
class?
- The Contained Feature Node class
and the Contained Within Feature
Face class form the two halves of the bidirectional topological
relationship between Feature Faces and
Feature Nodes. Whenever a
Feature Node appears as a component of a
Contained Feature Node component of a
Feature Face, that same
Feature Face must be associated with a
Contained Within Feature Face
component of that Feature Node and vice versa,
if the topology level is
3
or higher.
Constraints
Composed of (one-way)
Component of (one-way)
Prev: Contact Point.
Next: Contained Geometry Node.
Up:Index.

