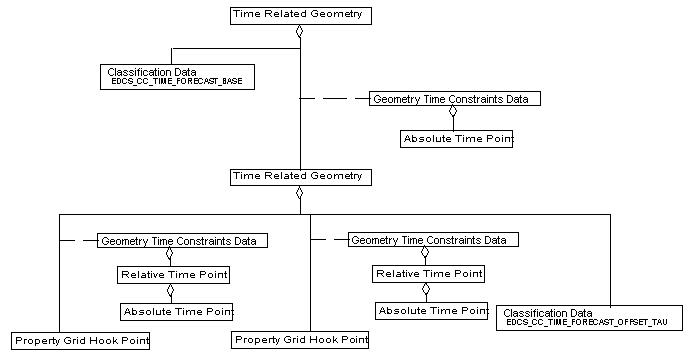
The Classification Data define what each Time Related Geometry corresponds to. The outer Time Related Geometry corresponds to base forecast times, while the inner Time Related Geometry corresponds to forecast taus.
In the forecast world, models are run starting at some base starting time, e.g., at 0Z and 12Z. The model then produces forecasts at several deltas after the base starting time, e.g. at 6, 12 ,18, and 24 hours. These are known as forecast taus.
Consequently, if you run forecast models at 0Z and 12Z, and each produces a 24 hour forecast, you get the following overlap.
16 Nov 17 Nov 18 Nov
0Z +6 +12 +18 +24
12Z +6 +12 +18 +24
0Z +6 +12 +18 +24
etc.
So to uniquely identify a forecast, you must specify the base forecast time and the delta (tau). This is why nested Time Related Geometry has been used in this example; one Time Related Geometry defines the base forecast time, while its component Time Related Geometry defines the forecast tau.
Note that this approach is needed only if multiple forecasts with overlapping forecasts are included in the transmittal. If we just use the analysis (0Z) and +6 forecasts from each forecast, then we would have
16 Nov 17 Nov 0Z +6 12Z +6 0Z +6 12Z +6 etc